Verify webhook signature
When the bot server receives a webhook event, verify the signature included in the request header before processing the webhook event objects. This verification step is important to confirm that the webhook came from the LINE Platform and wasn’t tampered with during transmission.
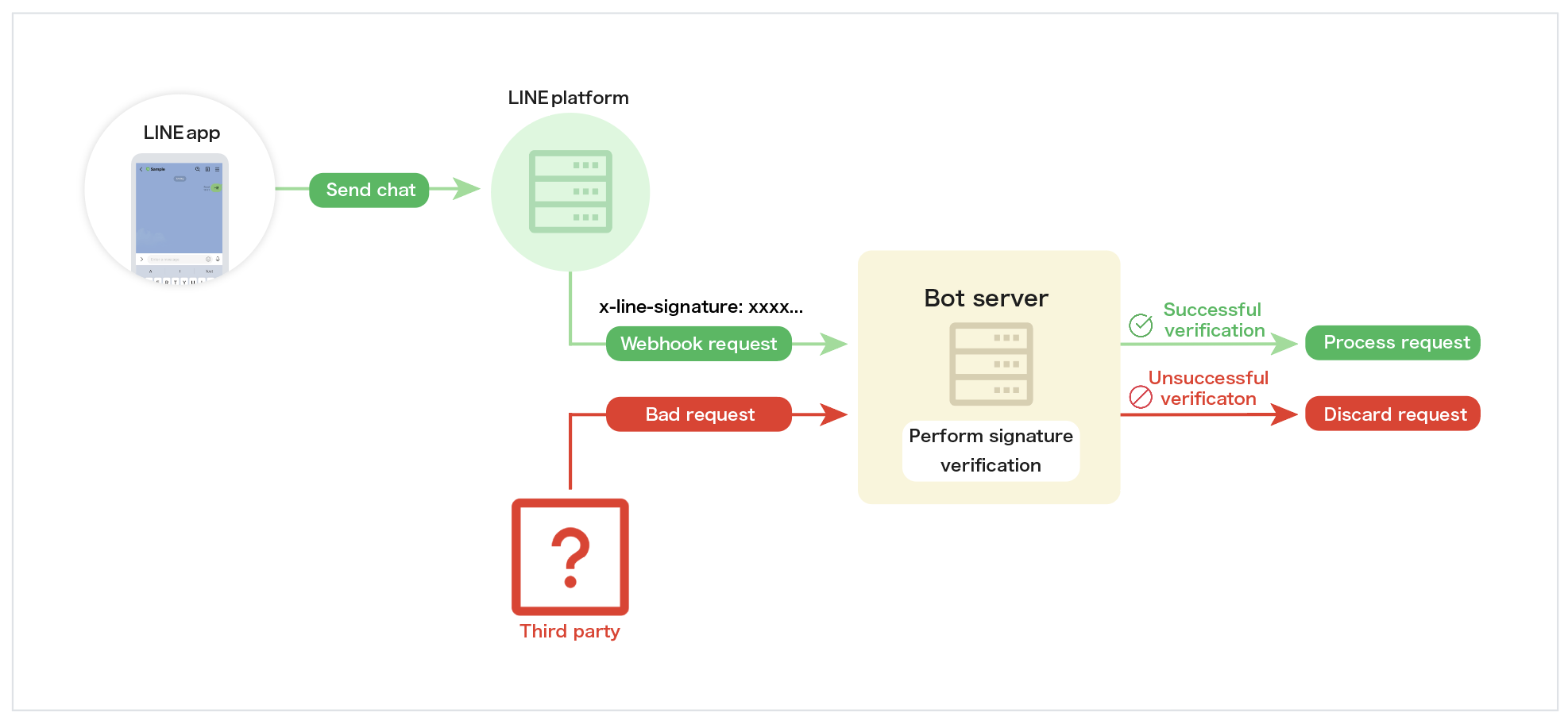
Verifying the webhook signature is an important security measure. Verifying the webhook signature is also recommended in the Messaging API development guidelines.
The IP address of the LINE Platform that sends the webhook isn't disclosed. Ensure security by verifying the signature rather than controlling access by IP address.
Preparations required for signature verification
To verify the webhook signature, you need the channel secret of the Messaging API channel.
Get Channel Secret
Open the channel's Basic settings tab in the LINE Developers Console and get the channel secret. You need Admin privileges for the channel to get the channel secret.
The channel secret is a private key known only to the LINE Platform and the developer. This channel secret is used as a hash key for signature verification and should be properly managed by the bot server.
Reissue Channel Secret
To reissue the channel secret, click Issue in the Basic Settings tab in the LINE Developers Console. If you are concerned that your channel secret has been compromised, reissue the channel secret. You need Admin privileges for the channel to reissue a channel secret.
Issuing a new channel secret invalidates the current channel secret. Before reissuing a channel secret, thoroughly investigate the impact on services that were using the existing channel secret.
The LINE Platform will not reissue a channel secret without the developer's consent.
How signature verification works
Signature verification means that both the webhook sender (the LINE Platform) and the receiver (the bot server operated by the developer) perform a calculation using the same hash key, and verify the legitimacy of the webhook by checking that the resulting signature matches.
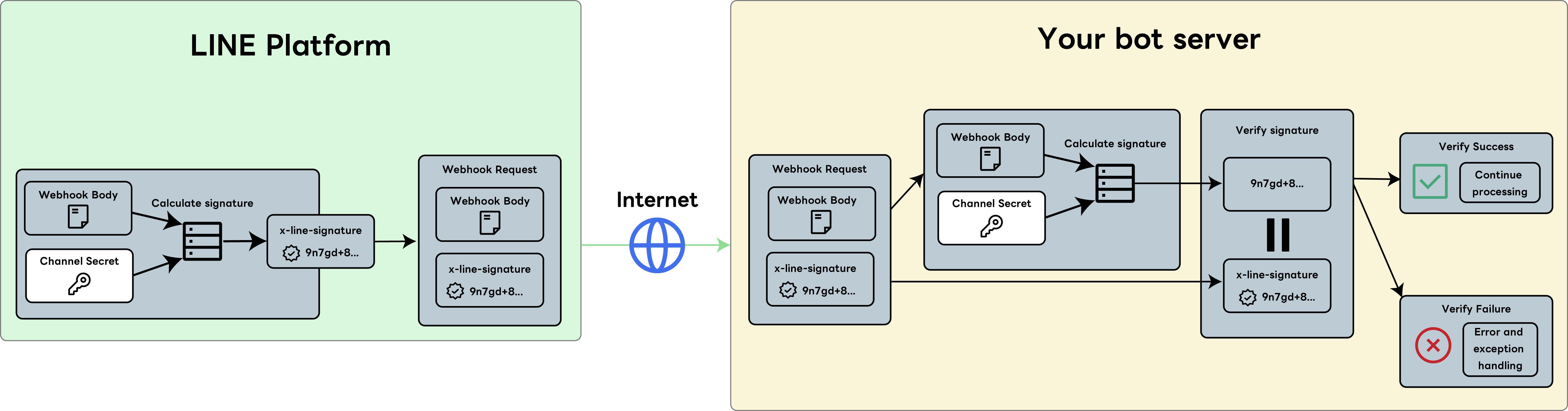
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how signature verification works.
- The LINE Platform sends a webhook to the bot server
- The bot server receives the webhook
- The webhook signature is verified on the bot server
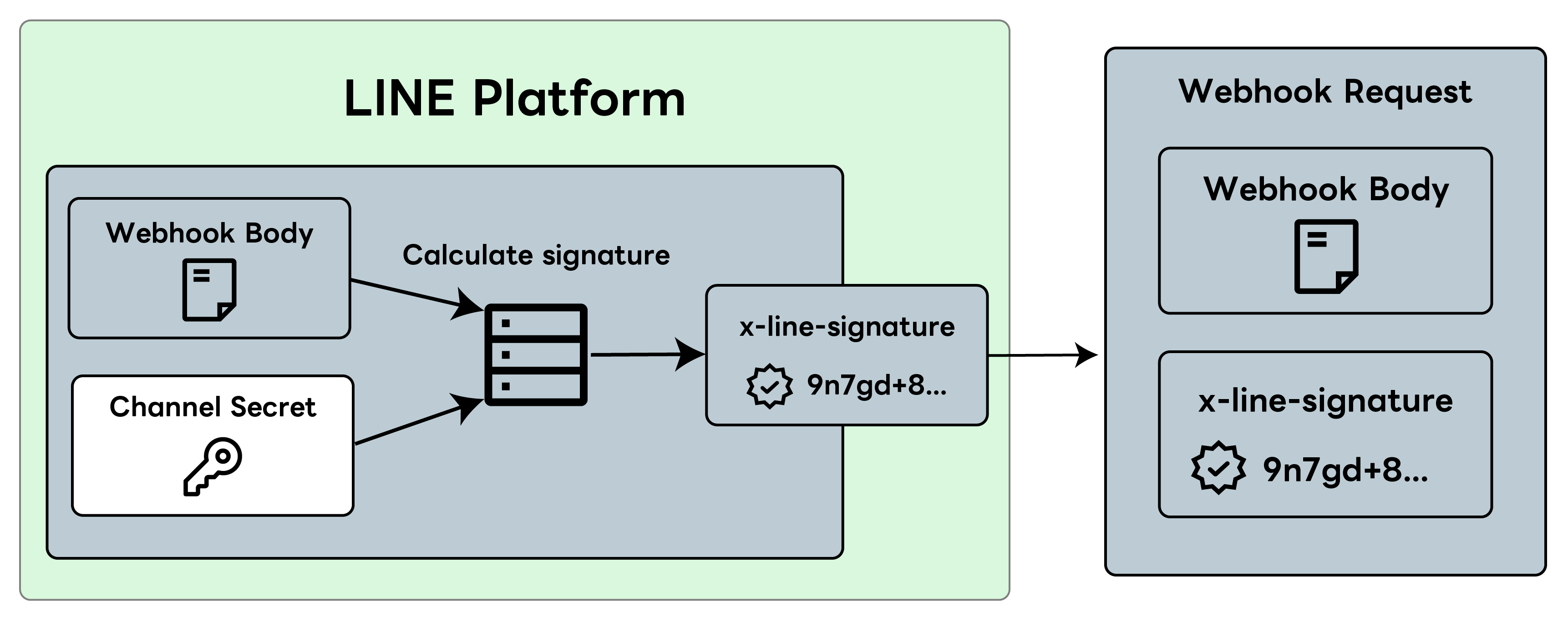
The LINE Platform sends a webhook to the bot server
The LINE Platform creates a signature when sending a webhook by following these steps:
- Generates a signature with HMAC-SHA256 using the webhook event as input data and the channel secret as the hash key.
- The generated signature is set to the
x-line-signatureheader. - Sends the webhook event and signature (
x-line-signature) to the bot server.
The bot server receives the webhook
The bot server gets webhooks from the LINE Platform.
Don't modify the signature (x-line-signature) in the request header of the received webhook, or the request body string, and store them as-is in the memory or database.
If any modification (string substitution, deserialization, escaping, etc.) is made to the signature or request body string prior to signature verification, it will be indistinguishable from a request that has been tampered with by a third party and signature verification will fail. It doesn't matter whether the request body string contains special escape characters such as backslash (\) or newline (\n). Don't modify data prior to verifying the signature on any request.
The webhook signature is verified on the bot server
The bot server verifies webhooks sent from the LINE Platform as follows:
- A signature is generated using HMAC-SHA256 with the string in the received Webhook request body as input data and the channel secret managed by the bot server as the hash key.
- Compares the received signature (
x-line-signature) with the generated signature. - If the signatures match, it's guaranteed that the received webhook was sent from the LINE Platform and reached the bot server without being tampered with.
- If the signatures match, take action based on the content of the webhook event.
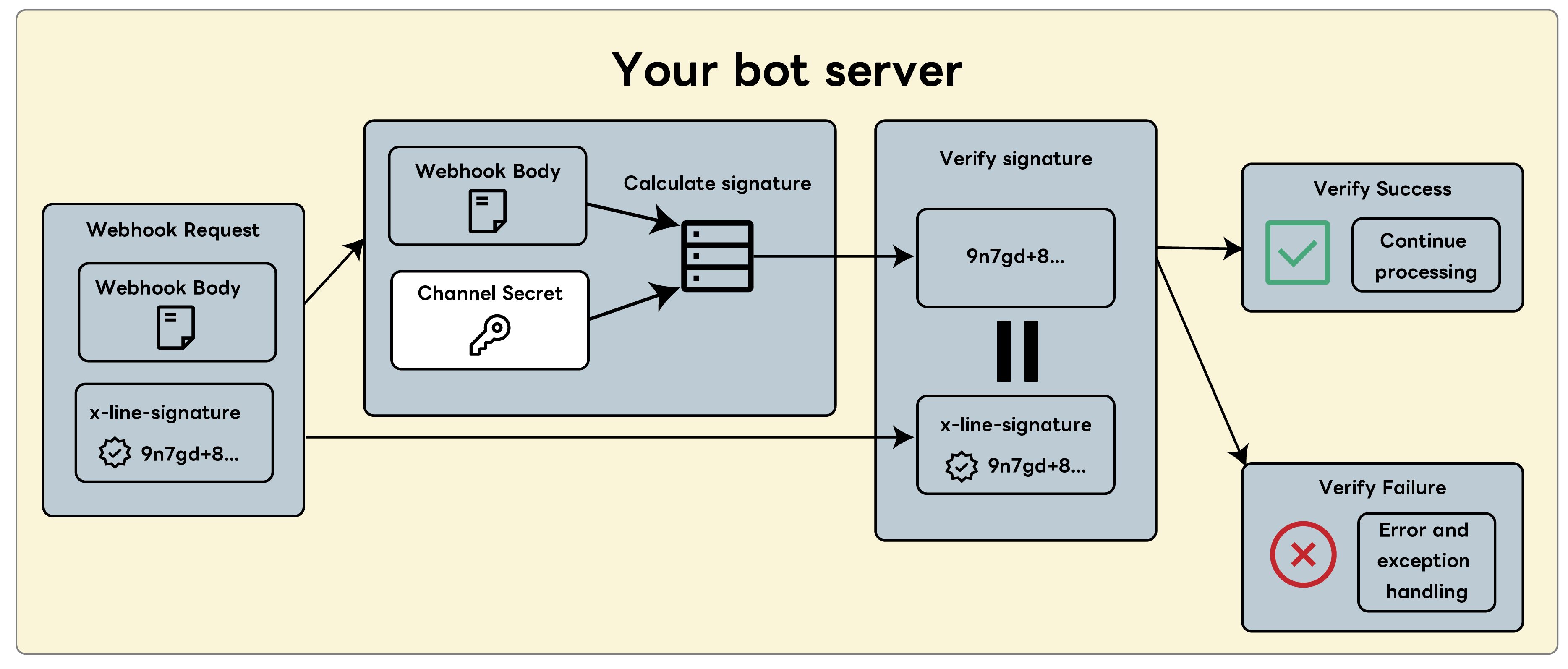
If the two signatures don't match or the signature isn't included in the webhook request header, don't process the webhook event and end the process with an error. If the signatures don't match, it may be due to these reasons:
- The request received by the bot server was sent from a source other than the LINE Platform
- The webhook received by the bot server has been tampered with by a third party
- There is an error in the way the bot server verifies signatures
If the webhook was sent from the LINE Platform, you can check the history of webhooks that you've tried to send in the LINE Developers Console under Statistics. For more information on how to check error statistics, see Check webhook error causes and statistics.
If the signatures don't match even though the webhook was sent from the LINE Platform, there may be an error in the way the signature is verified on the bot server. For more information, see Common signature verification failures and their solutions.
Signature verification procedure
Use the openssl command to review the signature verification procedure.
First, open the Messaging API tab for the channel from the LINE Developers Console and click Verify for the webhook URL to send a confirmation webhook from the LINE Platform.
- Webhook request body sent to the bot server
json
{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[]} - Signature (
x-line-signature) of the webhook sent to the bot servertextGhRKmvmHys4Pi8DxkF4+EayaH0OqtJtaZxgTD9fMDLs= - The channel secret for that channel
text
8c570fa6dd201bb328f1c1eac23a96d8 - Command to verify signature on bot server
sh
echo -n '{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[]}' | openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac '8c570fa6dd201bb328f1c1eac23a96d8' -binary | openssl base64 - Signature generated by the bot server
text
GhRKmvmHys4Pi8DxkF4+EayaH0OqtJtaZxgTD9fMDLs=
Since the signature of 2 received from the LINE Platform and the signature of 5 generated by the bot server match, we've confirmed that the webhook received by the bot server was sent from the LINE Platform and wasn't tampered with.
In actual development, you can easily verify the signature by using the LINE Messaging API SDK. See Signature validation in the Messaging API Reference for implementation examples in each language.
Common signature verification failures and their solutions
If the signature does not match even though the webhook was sent from the LINE Platform, there may be an error in the way the signature is verified on the bot server.
Below are some common reasons for signature verification failure and how to resolve them.
- Webhook changed before reaching the bot server
- Parsing and deserializing webhooks
- Incorrect formatting of the webhook request body string (JSON)
- An algorithm other than HMAC-SHA256 was used to verify the signature
- Used a channel secret for a different channel
- Another developer has reissued the channel secret
- Interpreted escape characters
- Character encoding used when processing webhooks wasn't UTF-8
Webhook changed before reaching the bot server
If you make any changes to the x-line-signature or request body strings of the webhook before signature verification, the signature verification will fail.
Make sure that no proxies or load balancers modify the request headers or body before the webhook reaches your bot server.
Parsing and deserializing webhooks
If you parse or deserialize the string in the received webhook request body and convert it to an object or array before verifying the signature, signature verification will fail.
- Webhook request body received by the bot server
json
{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[]} - Deserialize and output the webhook request body
python
decoded_data = json.loads('{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[]}') print(decoded_data) - Deserialization has changed double quotes to single quotes and/or introduced spaces
python
{'destination': 'U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0', 'events': []}
For signature verification, use the exact string in the received webhook request body.
Incorrect formatting of the webhook request body string (JSON)
If you format the JSON request body of the received webhook before verifying the signature to make it easier for developers to view, signature verification will fail.
- Webhook request body received by the bot server
json
{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[]} - Signature verification fails when webhook request body string (JSON) is formatted
json
{ "destination": "U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0", "events": [] }
For signature verification, use the exact string in the received webhook request body.
An algorithm other than HMAC-SHA256 was used to verify the signature
If an algorithm other than HMAC-SHA256 is used during signature verification, the signature verification will fail.
Check that you haven't mistakenly generated the signature using an algorithm other than HMAC-SHA256, such as HMAC-SHA1.
Used a channel secret for a different channel
If you use a channel secret for a channel other than the bot specified in the destination of the received webhook, signature verification will fail.
To verify the signature, both the sender of the webhook (LINE Platform) and the receiver (bot server operated by the developer) must perform calculations using the same hash key. The channel secret corresponds to this hash key, and is different for each channel.
Check the value of the Channel secret in the Basic settings tab of the LINE Developers Console.
Another developer has reissued the channel secret
When a new channel secret is issued in the Basic settings tab of the LINE Developers Console, the previous channel secret becomes invalid.
If signature verification that was previously working suddenly starts failing, it's possible that another developer with admin privileges for the same channel has reissued the channel secret.
Check the current channel secret value in the Basic settings tab in the LINE Developers Console. If the channel secret was reissued, the channel secret used for signature verification on the bot server must be replaced with the new one.
Interpreted escape characters
The request body of a received webhook may contain special escape characters such as backslash (\) or newline (\n). If escape characters are not handled and interpreted as they are, signature verification will fail.
For example, when using the echo command in a local environment to check the operation of signature verification, enclose the escape characters in single quotes instead of double quotes, so that they are treated as they are.
echo -n '{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[]}' | openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac '8c570fa6dd201bb328f1c1eac23a96d8' -binary | openssl base64
In Python, you can use raw string literals (r"...") to handle escape characters as they are.
body = r'{"destination":"U8e742f61d673b39c7fff3cecb7536ef0","events":[{"type":"message","text":"hello\ntest1\ntest2"}]}'
When verifying the signature, don't interpret escape characters and use the string in the received webhook request body as is.
Character encoding used when processing webhooks wasn't UTF-8
Webhooks from the LINE Platform are sent in UTF-8 encoding (Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8).
When verifying the signature using the received webhook request body, if the data is processed in an encoding other than UTF-8, the line break code may change from LF (\n) to CRLF (\r\n), emojis and special characters (tabs, control characters, etc.) may be misinterpreted, and signature verification will fail.
When verifying a signature, make sure that the character encoding is UTF-8.

